Science helps tailor livestock-related climate change mitigation strategies in Africa
- From
-
Published on
17.07.18
- Impact Area
-
Funders
EU Commission, IFAD
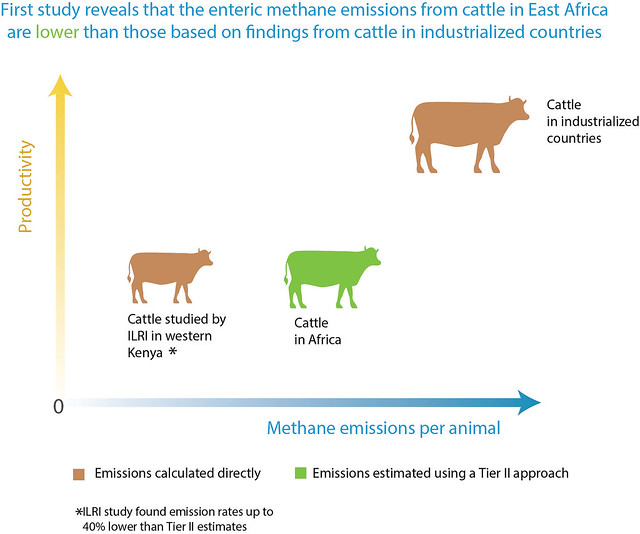
 Livestock contribute greatly to livelihoods and food security in Africa, yet they are both vulnerable to climate change and a major contributor to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, a known driver of climate change. Climate change is expected to alter the quantity and quality of available animal feed and impact livestock directly through increased heat stress, changes in water availability and a greater range of livestock diseases. And higher levels of poverty in Africa exacerbate the effects of GHG-induced climate change on vulnerable populations.
Livestock contribute greatly to livelihoods and food security in Africa, yet they are both vulnerable to climate change and a major contributor to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, a known driver of climate change. Climate change is expected to alter the quantity and quality of available animal feed and impact livestock directly through increased heat stress, changes in water availability and a greater range of livestock diseases. And higher levels of poverty in Africa exacerbate the effects of GHG-induced climate change on vulnerable populations.
Existing estimates suggest that the livestock sector in Africa contributes to more than 70% of the continent’s agricultural GHG emissions, mainly due to methane and nitrous oxide emissions, two particularly potent GHGs, predominantly from cattle and their manure. The implementation of effective mitigation strategies relies on accurate GHG emission data. But what if the underlying assumptions upon which these GHG emission estimates are based are inaccurate?
![]()
Related news
-

Strengthening One Health through rangelands stewardship
Multifunctional Landscapes Science Program04.12.25-
Climate adaptation & mitigation
HEAL community rangeland health workers presented at the 33rd Annual Conference of the Ethiopian Soc…
Read more -
-

Innovative Aloe vera ventures: Community Rangeland Health Workers paving the way for healthy people and healthy rangelands
Multifunctional Landscapes Science Program04.12.25-
Climate adaptation & mitigation
The One Health approach connects the health of humans, animals, and the environment. By fostering…
Read more -
-

How District Technical Working Groups are Reviving Cambodia’s Floodplain Ecosystems
Scaling for Impact Program04.12.25-
Climate adaptation & mitigation
By Sao Sok, WorldFish & Sanjiv De Silva, IWMI Cambodia’s diverse natural ecosystems remain cen…
Read more -